How to Grow Stock Flower Plants
The stock flower plant (Matthiola incana) is a species in the Brassicaceae (cabbage) Family. It is a common flowering plant in the gardening industry. The flowers of these plants are heavily scented and bloom in various colors. Most widely, these flowers are used in floristry.
This article primarily focuses on stock flower plants, their propagation, caring, varieties, and uses.
Stock flower plant is indigenous to southern European regions. You can find these plants growing in abundance from Balearics to the lush lands of former Yugoslavia. Over time, these coastal plants have naturalized in western Mediterranean regions including hinterlands at altitudes of about 600 meters.
These plants also have several other names including Gilly-flower, common stock, ten-week stock, Brompton stock, and hoary stock.
The Latin name of this plant is speculated to commemorate Peter Matthioli. (King Ferdinand 1’s personal physician in Austria during the 16th century). This information is available in ‘The Leisure Hour’s 1905 article, “Memorial plant names”. In fact, ‘The Leisure Hour’ itself is a Victorian-era British periodical magazine.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Stock Flower Plants

Depending on the regions, you can grow stock flower plants as perennials, or annuals.
Generally, it is a cool weather plant. It blooms usually from spring to summer. For setting healthy buds, these plants require temperatures below 60 degrees Fahrenheit. As the temperature rises, they may set fewer buds or even stop setting.
These plants grow as annuals in cooler regions (USDA Zones 6 or below). They can also withstand the initial frosts. Hence, some people term as “half-hardy”. Usually, the growers start the propagation during spring, in these locations.
In warmer areas (USDA Zones 7 – 10), these plants grow as perennials. Each spring, they grow back with mediocre woody stems. They bloom till summer. When the temperature becomes extremely hot, they stop blooming. Usually, the growers start the propagation during fall, in these regions.
As perennials, they tend to bloom and start setting seed from the second year. This character can also be termed as “biennial”.
Description of Stock Flower Plants
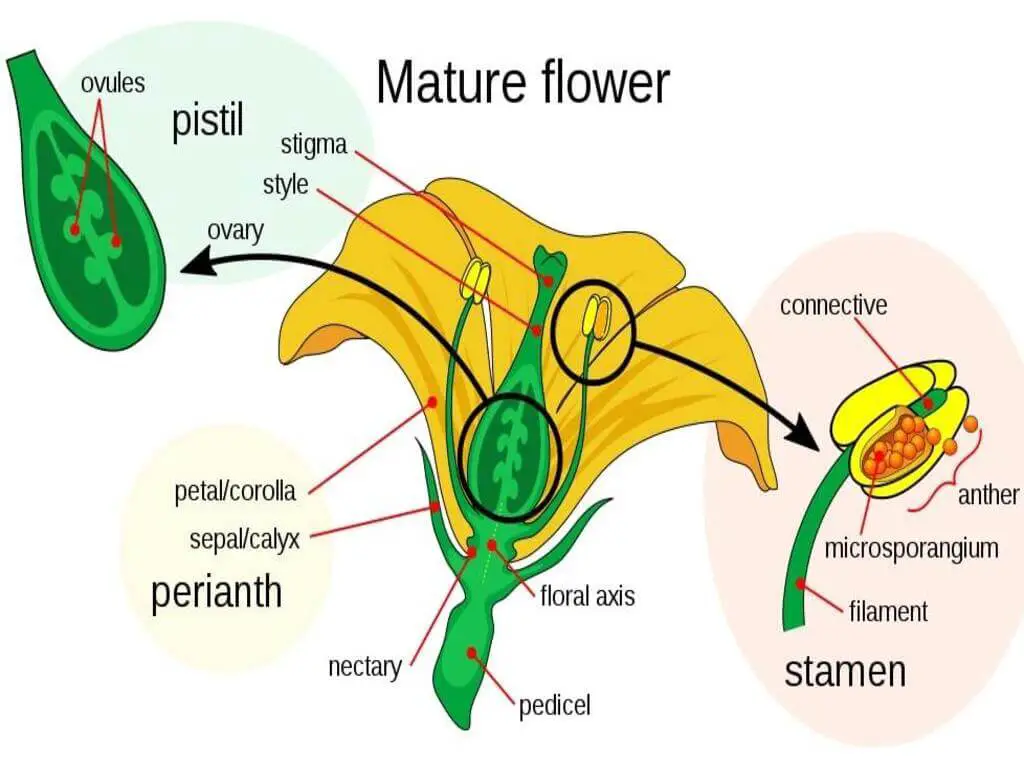
Some annual varieties of stock flower plants can grow in excess of 3 inches in height. The woody stems measure 20 – 28 cm across in diameter. The branches have a circular arrangement of leaves (rosettes). Usually, these lanceolate, attenuated leaves have an ash-color.
The plants themselves have a starry appearance with white or cream hairs. The heavily scented flowers have a variety of colors including cream, white, yellow, red, pink, blue, or purple.
The compressed, small pods have flattened flaps. During the anthesis period, pedicels measure about 10-12 mm. Similarly, they measure about 12-17 mm while fruiting.
The green sepals measure about 11-14 mm. The individual petals measure about 25-30 mm long. The suborbicular seeds are about 2-3 mm long.
Propagation of Stock Flower Plants
Generally, the stock flower plants prefer to grow under full sun. They can tolerate partial afternoon shaded also. They also prefer loose, rich, slightly alkaline, and well-draining soil. Before planting, it is advisable to amend the soil with a general fertilizer.
From Seeds
The stock flower seeds are easy to purchase. They are available on amazon. You can also buy from other online stores or your local offline nursery! After that, you can start the propagation initially indoors, 7 – 8 weeks prior to the last frost date.
1.) Start sowing the seeds slightly below the surface in a pot filled with vermiculite.
2.) Water the sowed seeds thoroughly.
3.) Place the pot in a room that gets plenty of indirect sunlight. If such space is not available, you can also use Grow lights.
4.) Maintain the soil moist by watering regularly.
If the temperature lies consistently about 53 to 64°F (12-18° C), you can expect germination in about a couple of weeks. After that, transplant them at the outer spaces in late spring or autumn.
Alternatively, you can sow the seeds directly in the garden after the frost. The propagation procedure for this method is also the same as stated above.
Make sure, the distance between the plants is at least 6 inches. Some larger spread varieties may need about 18 inches distance between them.
From Cuttings
You can also grow the stock flower plants from cuttings. If you already grow them, collect the cuttings from your garden. Else, you can request your known gardeners.
Usually, most gardeners start cutting propagation in summer.
1.) Snip off the shoots about an inch from the ground, using garden shears
2.) Remove the foliage from the bottom half of the cutting
3.) Gently dip the bottom end in rooting hormone.
4.) Place the cutting in a hole dug at least an inch deep in an upright position. Then backfill the soil
5.) Water the arrangement fully. Makes sure to maintain the soil moisture by watering regularly.
You can expect the cuttings to root in about a couple of weeks.
Caring of Stock Flower Plants

Fertilize the plant every month to encourage its healthy growth.
By watering twice a week or so, maintain the soil moderately moist to slightly dry. Water the plant at the bottom in the mornings. This gives the plant time to dry using the day time heat. Avoid vaguely pouring water on the foliage. For efficient watering, we recommend you to use drip and trickle systems.
Using a good quality weed remover, remove the weeds regularly. They can compete with plants for water and also invite undue pests. Mulching helps to keep weed growth under check. It also helps maintain soil temperature to some extent.
Pruning
Initially, the stock flowers bloom open from the bottom of the flowering stack and continue towards the tip. Hence, the bottom flowers fade first followed by the consecutive upper ones. If the browning look bothers you, simply snip off the individual dead flowers.
When all the flowers fade, remove the flower spike as a whole from the lateral bud.
During hot summers, prune the stock flower plant to its woody basal. This encourages fresh growth during the following growing season. We recommend you to use good quality garden shears for every pruning activity.
Varieties of Stock Flower Plants
For several years, the stock flowers have been bred into various cultivars. Nowadays, you can easily find more than 60 known types of cultivars in floral markets. In addition, many unknown hybrids are cultivated by private growers and researchers for their due purpose. we have listed some of the popular stock flower varieties below
Starlight Sensation Stock
The starlight sensation grows up to 8 inches in height. This cultivar blooms in a wide range of colors. in fact, you could not guess what colored flower your plant will develop before it does. But you can expect an abundance of fragrant, large single blooms in spring and summer.
White Goddess Stock
If you prefer to grow one of the world’s best visually elegant flowers, the white goddess stock is a perfect choice! Each flower stack develops two flowers (double blooms). These large white flowers have a sweet fragrance. This variety is one of the bestselling flowers in the gardening industry.
Legacy Stock
There are many hybrids in the Legacy series. All of them grow about two feet in height. They sprout beautiful double blooms in different colors. Their signature sweet and spicy fragrance is very popular among the masses. Out of the best-selling varieties in the world, the legacy series of stocks have a commendable share.
Cinderella Stock
If you prefer dwarf stocks with traditional colors and signature smells, the Cinderella stock can be your best choice! Normally, this stock grows about 10 inches tall and sprouts beautiful double blooms. If you have nose-high containers in your gardens or indoors, Cinderella stocks can serve better than almost any other flowering plant, with its beauty and perfume.
Pests and Diseases
Diseases
Botrytis
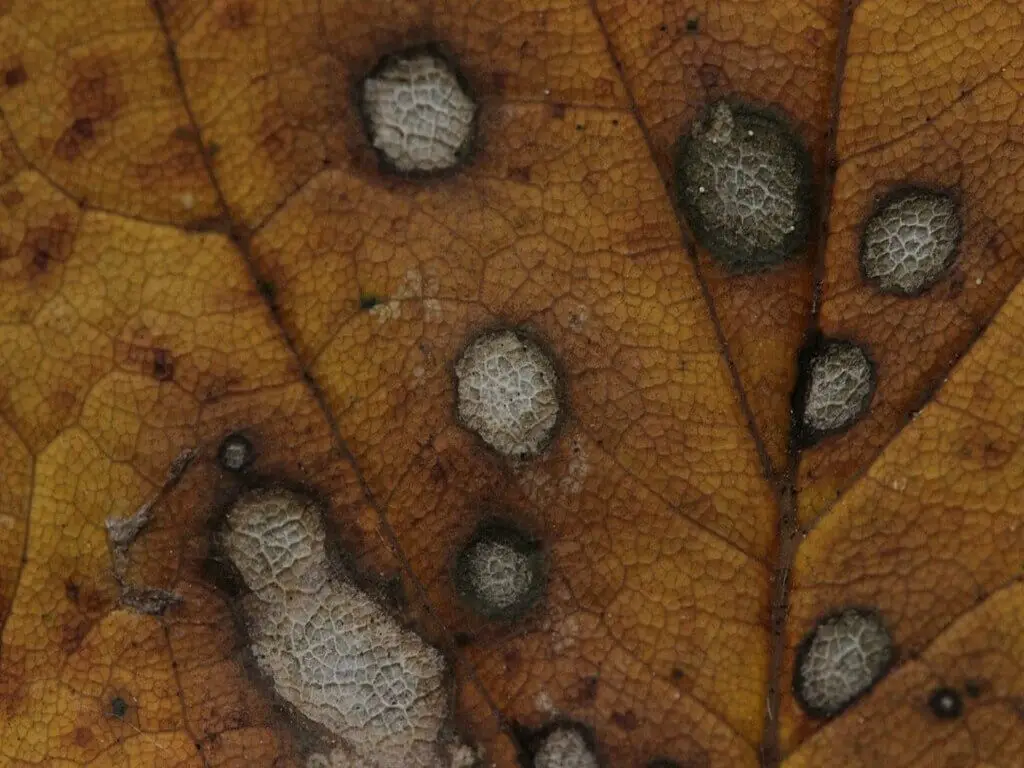

Photo by Björn S (Wikimedia Commons) (CC BY-SA 2.0)
This fungus affects plants in wet environments, particularly in cool climates. The infected parts of the plant develop a grey mold. Later, the disease-causing spores spread through wind and water to new plants.
In the initial stages, you can try copper fungicides. But if the infection is huge, destroy the plants immediately.
Prune the plants periodically. keep the surroundings debris free. This helps in the prevention of the disease.
Root rots
When the plant is surrounded by waterlogging, root rot disease is inevitable in most cases. Always grow the plants in well-draining soils.
If the disease is minimal, you can cut off the infected part of the root with sterilized shears. Replant the plant in fresh, well-draining soil. But, if the damage is excess, destroy and dispose of the plant immediately.
Alternaria Leaf Spot
This disease infects plants mostly in warm and humid environments. The infected foliage develops small reddish spots with whitish centers. The lesions may cause the infected parts to wilt.
You can use a fungicide to treat this disease. However, practice sanitation and rotation of crops to prevent future infection.
Verticillium wilt
Verticillium wilt is caused by a soil-borne fungus. Initially, it enters from the roots and spreads through the vascular system. The infected foliage first turns yellow them wilts. The infected branches wilt slowly or suddenly depending on the infection intensity.
Since there is no effective treatment available, remove and destroy the whole plant.
Pests
Aphids
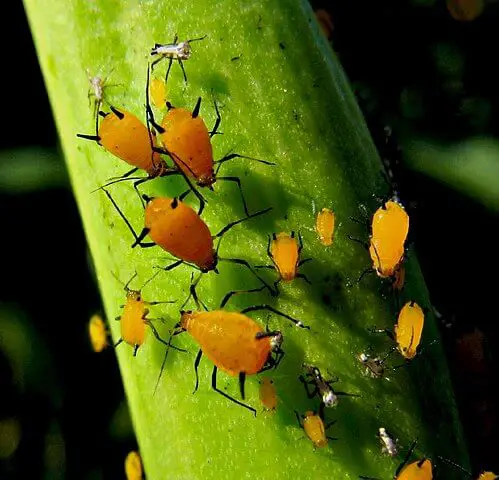

Photo by aroid (Wikimedia Commons) (CC BY 2.0)
These common plant pests have different colors including green, black, peach, and red. They act as carriers or vectors’ and spread disease pathogen among plants. In addition, they suck the foliage sap thereby damaging plants and reducing yields. Their honeydew is known to attract other harmful pests.
You can use a strong blast of hose water to wash them away. You can also treat them effectively with neem oil sprays or aphid sprays.
Flea Beetles
These small flies are also called jumping beetle. While feeding on foliage, they make small holes that damage them heavily. Tender seedlings may even die due to this act. Moreover, flea beetles act as “vectors” in spreading plant diseases.
You can treat flea beetles and most other beetles effectively with Diatomaceous earth.
Spider Mites
Spider mites are tiny insects with a spider-like appearance. They appear in various colors including black, brown, yellow, or red. These insects suck the foliage sap out, remove chlorophyll and also inject toxins. As a result, the infected foliage develops white dots and finally wilts.
You can wash them away with a strong blast of water from the hose. You can also treat them effectively with Neem oil sprays and diatomaceous earth.
Whitefly
Whiteflies are small in nature. By sucking sap, they cause decolorization and stunted growth in foliage. In addition, their honeydew attracts other pests.
You can treat whiteflies effectively with horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps.
Uses
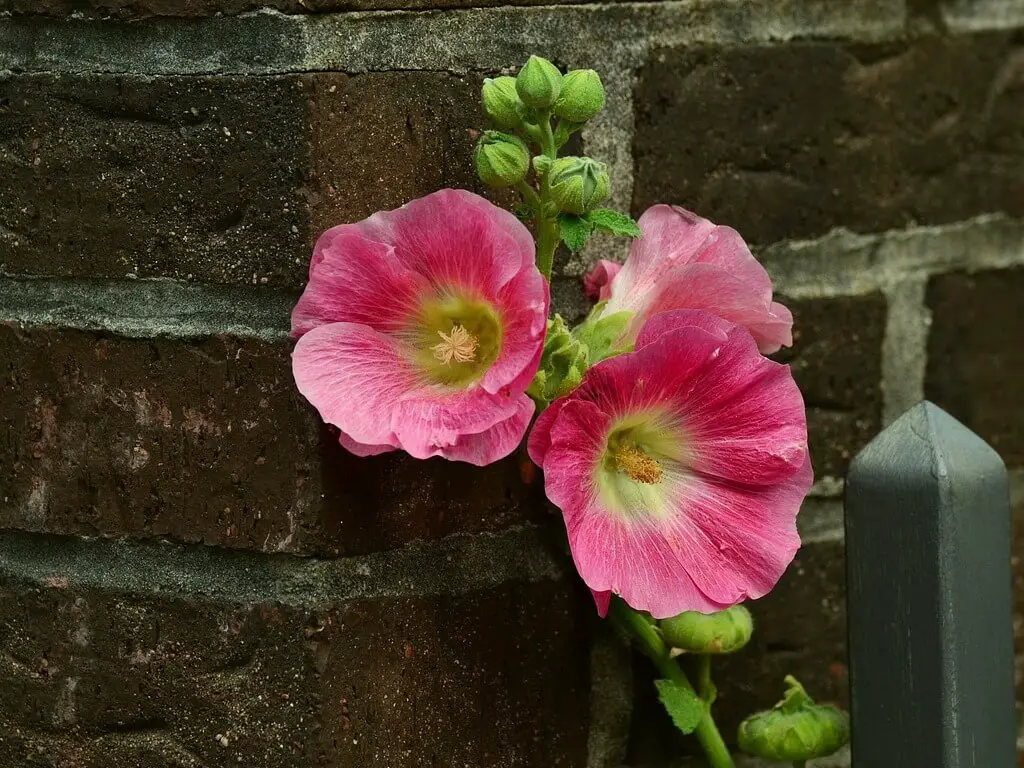

The stock flowers are excellent additions to beautiful gardens. Most designers prefer these plants for edging or bordering lawns. Due to their tall blooming habits, you can plant them at the back of your flower beds.
Due to stocks of sweet and spicy perfume, some florists make it a compulsory addition to flower bouquets. Similarly, their vibrant colors make them a welcome addition to the cut flower arrangements for indoor decorations.
Make sure to plant the dwarf varieties in front and other varieties at back. They will never fail to decorate your spaces beautifully.
Similar Posts
How to Grow Parrot Tulips in Gardens
How to Grow Blue Balloon flower (Platycodon Grandiflorus) Plants?

